Object |
Shared with other SmartSolve© Applications |
Required for SmartCAPATM |
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
Object |
Shared with other SmartSolve© Applications |
Required for SmartCAPATM |
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
No |
Object |
Shared with other SmartSolve© Applications |
Required for SmartCAPATM |
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
No |
No |
Object |
Shared with other SmartSolve© Applications |
Required for SmartCAPATM |
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
Object |
Shared with other SmartSolve© Applications |
Required for SmartCAPATM |
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
No |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
Object |
Shared with other SmartSolve© Applications |
Required for SmartCAPATM |
|
No |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
No |
Yes |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
Object |
Shared with other SmartSolve© Applications |
Required for SmartCAPATM |
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
Object |
Shared with other SmartSolve© Applications |
Required for SmartCAPATM |
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
|
|
No |
No |
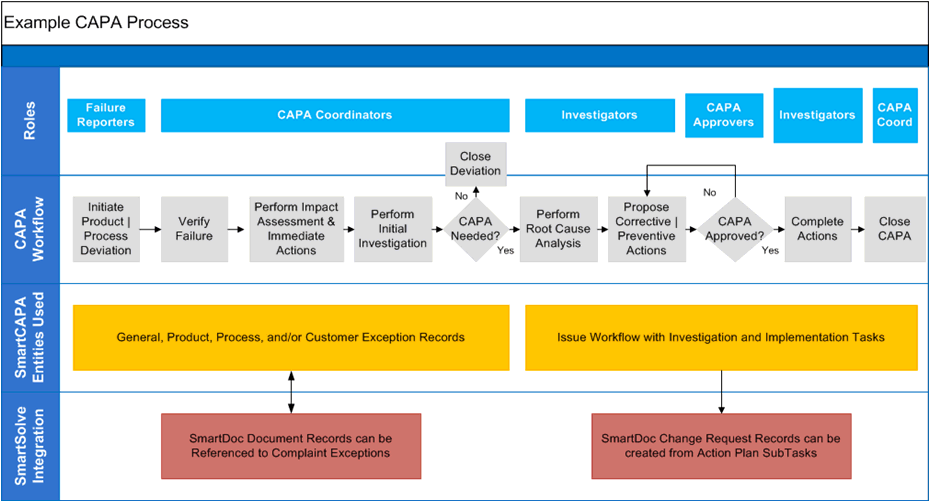
As an administrator it is important to become familiar with the various setup and policy tables available off the shelf with SmartCAPATM.
Please see the SmartCAPATM End User Guide for more information on SmartCAPATM end user functions and how to maintain end user records once the system is configured for use.
Prior to configuring the SmartCAPATM system it is very important to meet with the key stakeholders of the SmartCAPATM application. You should discuss exactly what business requirements must be met in the system, who is responsible for these requirements, and the standards for the completed requirements.
This common practice is not only needed to configure the SmartCAPATM system successfully; but also helps Pilgrim customer’s to revisit their business processes and work to ensure that these processes are effective and efficient (continually improved to ensure processes use the least amount of resources).
Some important things to consider when implementing SmartCAPATM:
It helps a great deal to start with one simple model and build your configurations from this one scenario, then you can pull in the rest of your scenarios after testing the scenario to see if these configurations will work. Trying to do everything at one time causes proven delays in your implementation so keep it simple!
How many other SmartSolve© systems will, or have already been implemented within your organization?
If any other systems have already been implemented, obtain a copy of the Software Requirements Specification (configuration documentation) and refer to this documentation as well as collaborate with other SmartSolve© administrators on how these other SmartSolve© systems were configured.
It is important when process mapping to try not to figure out “what” is going to go “where” in the SmartCAPATM system yet; but to make sure the business requirements are clearly illustrated.
Map out a process flow for reporting an exception (i.e., product nonconformance) and discuss the following:
Define the type of event (exception) you wish to start with and how event will be recorded (by end user reporter, or imported from other third
party application using the SmartSolve Synchronization Agent - SSA.
Identify all entry fields required for reporting the exception (i.e., products, failure modes, business entities involved, etc,).
Map out the process for managing the exception (who will own the exception and oversee it throughout its life cycle).
Determine when you may need to create an Issue from the exception record (if applicable).
Illustrate the different steps performed by various user roles to record and resolve the exception and issue (step sequence from simple resolution to most complex model for resolving, for example Product Disposition, Initial Investigation, CAPA).
Determine how exceptions and issues will be looked up (Advanced Searches) and how information will be analyzed through reports (queries), etc.

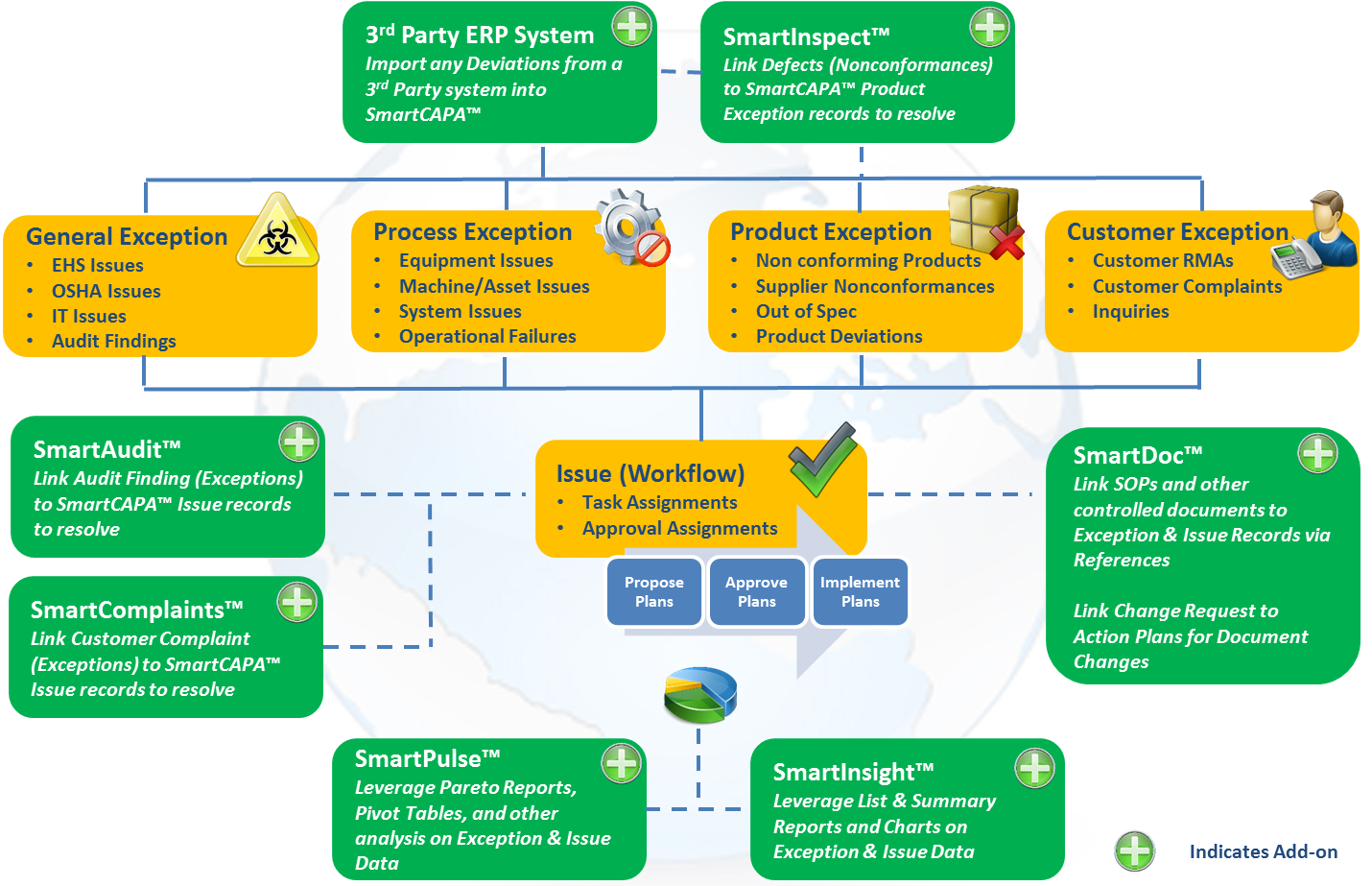
Anyone can submit an exception. Exceptions can come from customers, end users, or distribution partners, etc. The importance of the exception record in SmartCAPATM is having the ability to track, record, classify and trend all the exceptions that are submitted.
The illustration below shows some of the different ways in which exceptions could be reported in SmartCAPATM:
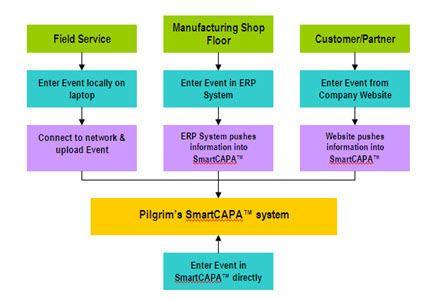
The scenarios below explain a little more in-depth how the complaint reporting examples above could be carried out using SmartCAPATM:
Scenario |
Description |
|
Field Service Scenario |
People in the field (i.e., auditor) could have the data entry form on their lap tops so that they could enter the information into their template while in the field. Once back in the office, they connect to the network (within the office or via VPN connection), access the solution over the server, then synchronize and upload the information into the SmartCAPATM exception record.
|
|
Manufacturing Shop Floor Scenario |
Product and/or process failures may be recorded from the manufacturing floor during product testing, inspections, audits, etc. In such cases, a plant supervisor, inspector, or operator may typically enter the information locally in to their ERP system (i.e., MES). The ERP system would then synchronize with SmartCAPATM and push the information into the SmartCAPATM record.
|
|
Customer/Partner Scenario |
Customers/clients may also submit their events directly through your company website. The information which is entered through the web site can then be pushed into SmartCAPATM to be managed and resolved through the SmartCAPATM record.
|
|
NOTE: These approaches would require interfacing with systems such as ERP systems or web sites. However, the event can also be entered manually by the user. The next step in the process is recording an exception (event) in SmartCAPA with all required information and validated data. |